2. Applied Physics : Measurement Units and Dimension; Waves, Acoustics,Ultrasonic, Light Laser and its Application, Atomic Structure and Energy Levels.
Sample Questions
Questions on Measurement Units and Dimension:
Which of the following pairs is wrong. [AFMC 2003]
a)Pressure-Baromter
b) Temperature-Thermometer
c) Relative density-Pyrometer
d) Earthquake-Seismograph
Ans is: Relative density-Pyrometer
Ques: In which of the following systems of unit, is the unit of magnetic flux .
a) CGS
b) SI
c) MKS
d) None of these
Ans is Si
Ques: Universal time is based on
a) Rotation of the earth on its axis
b) Vibrations of cesium atom
c) Earth's orbital motion around the earth
d) Oscillations of quartz crystal
Ques: Which of the following affects the absorption of sound in a room:
a)the material used for wall surfaces.
b)the number of people in the audience.
c)the volume of air in the room.
d)all of the above.
Ques: If two pure tone sound waves in air differ by an octave,
a)one has twice the frequency of the other.
b)one has twice the wavelength of the other.
c)they differ by 1200 cents.
d)all of the above.
3. Basic Electricity : Electrostatics, Coulomb’s law, Electric field, Gauss’s theorem,concept of potential difference; concept of capacitance and capacitors, Ohm’s law, power and energy, Kirchoffs voltage, current laws and their applications in simple DC circuits, Basic Magnetism, Electro Magnetism, Electromagnetic Induction, Concept of alternating voltage & current Cells and Batteries, Voltage and Current Sources. Thevenin’s theorem, Norton’s theorem and their applications.
Do you know?
Coulomb's law is used for describing the electrostatic interaction between electrically charged particles.
Gauss's law, also known as Gauss's flux theorem, is a law relating the distribution of electric charge to the resulting electric field.
Gauss's law states that
The net outward normal electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the total electric charge enclosed within that closed surface.
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points
Kirchoffs Laws: Study from Wikipedia about these topics
There are two laws
Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) & Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL)
Law I: Kirchhoff's first law, Kirchhoff's point rule
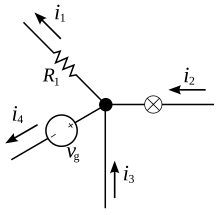
This law explains than the sum of all the currents meeting at any point is zero.In the above Diagram the Sum of all the currents i1 + i2 + i3 + i4 = 0 or i1 + i2 = i3 + i4
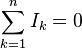
Law II: Kirchhoff's second law, Kirchhoff's loop (or mesh) rule
Sample Question
Ques: What is a series circuit?
a) a circuit containing two or more resistors
b) a circuit with only one current path
c) a circuit containing two or more voltages that are equal in val
d) none of these
Ques: Which of the following statements is true?
a) Kirchhoff's voltage law states that the algebraic sum of the voltages around a closed loop must equal zero.
b) Kirchhoff's voltage law allows us to calculate the voltage across a given resistor without knowing the value of the source voltage.
c) Kirchhoff's voltage law states that the algebraic sum of all of the voltages around a closed loop must equal the source voltage.
d) None of these
Ques: Which of the following statements is true?
a) Source resistance mainly affects low-current loads.
b) Source resistance mainly affects low-resistance loads.
c) Source resistance mainly affects high-resistance loads.
Sample Questions
Questions on Measurement Units and Dimension:
Which of the following pairs is wrong. [AFMC 2003]
a)Pressure-Baromter
b) Temperature-Thermometer
c) Relative density-Pyrometer
d) Earthquake-Seismograph
Ans is: Relative density-Pyrometer
Ques: In which of the following systems of unit, is the unit of magnetic flux .
a) CGS
b) SI
c) MKS
d) None of these
Ans is Si
Ques: Universal time is based on
a) Rotation of the earth on its axis
b) Vibrations of cesium atom
c) Earth's orbital motion around the earth
d) Oscillations of quartz crystal
Ques: Which of the following affects the absorption of sound in a room:
a)the material used for wall surfaces.
b)the number of people in the audience.
c)the volume of air in the room.
d)all of the above.
Ques: If two pure tone sound waves in air differ by an octave,
a)one has twice the frequency of the other.
b)one has twice the wavelength of the other.
c)they differ by 1200 cents.
d)all of the above.
Ques: The lowest few partials of a tone are 220 Hz, 440 Hz, 660 Hz, and 880 Hz. Which of the following is true?
a)The third harmonic is 660 Hz.
b)The fourth overtone is 880 Hz.
c)The fundamental frequency is 110 Hz.
d)All of the above.
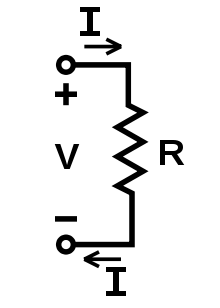
Basic diagram showing Current, Voltage & Resistance
V=IR

Do you know?
Coulomb's law is used for describing the electrostatic interaction between electrically charged particles.
Gauss's law, also known as Gauss's flux theorem, is a law relating the distribution of electric charge to the resulting electric field.
Gauss's law states that
The net outward normal electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the total electric charge enclosed within that closed surface.
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points
Kirchoffs Laws: Study from Wikipedia about these topics
There are two laws
Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) & Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL)
Law I: Kirchhoff's first law, Kirchhoff's point rule

This law explains than the sum of all the currents meeting at any point is zero.In the above Diagram the Sum of all the currents i1 + i2 + i3 + i4 = 0 or i1 + i2 = i3 + i4
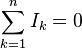
Law II: Kirchhoff's second law, Kirchhoff's loop (or mesh) rule

Here, n is the total number of voltages measured. The voltages may also be complex:
Ques: What is a series circuit?
a) a circuit containing two or more resistors
b) a circuit with only one current path
c) a circuit containing two or more voltages that are equal in val
d) none of these
Ques: Which of the following statements is true?
a) Kirchhoff's voltage law states that the algebraic sum of the voltages around a closed loop must equal zero.
b) Kirchhoff's voltage law allows us to calculate the voltage across a given resistor without knowing the value of the source voltage.
c) Kirchhoff's voltage law states that the algebraic sum of all of the voltages around a closed loop must equal the source voltage.
d) None of these
Ques: Which of the following statements is true?
a) Source resistance mainly affects low-current loads.
b) Source resistance mainly affects low-resistance loads.
c) Source resistance mainly affects high-resistance loads.
d) None of these

No comments:
Post a Comment